Medication induced fetal bladder rupture: a case report
4.5 (706) In stock

4.5 (706) In stock
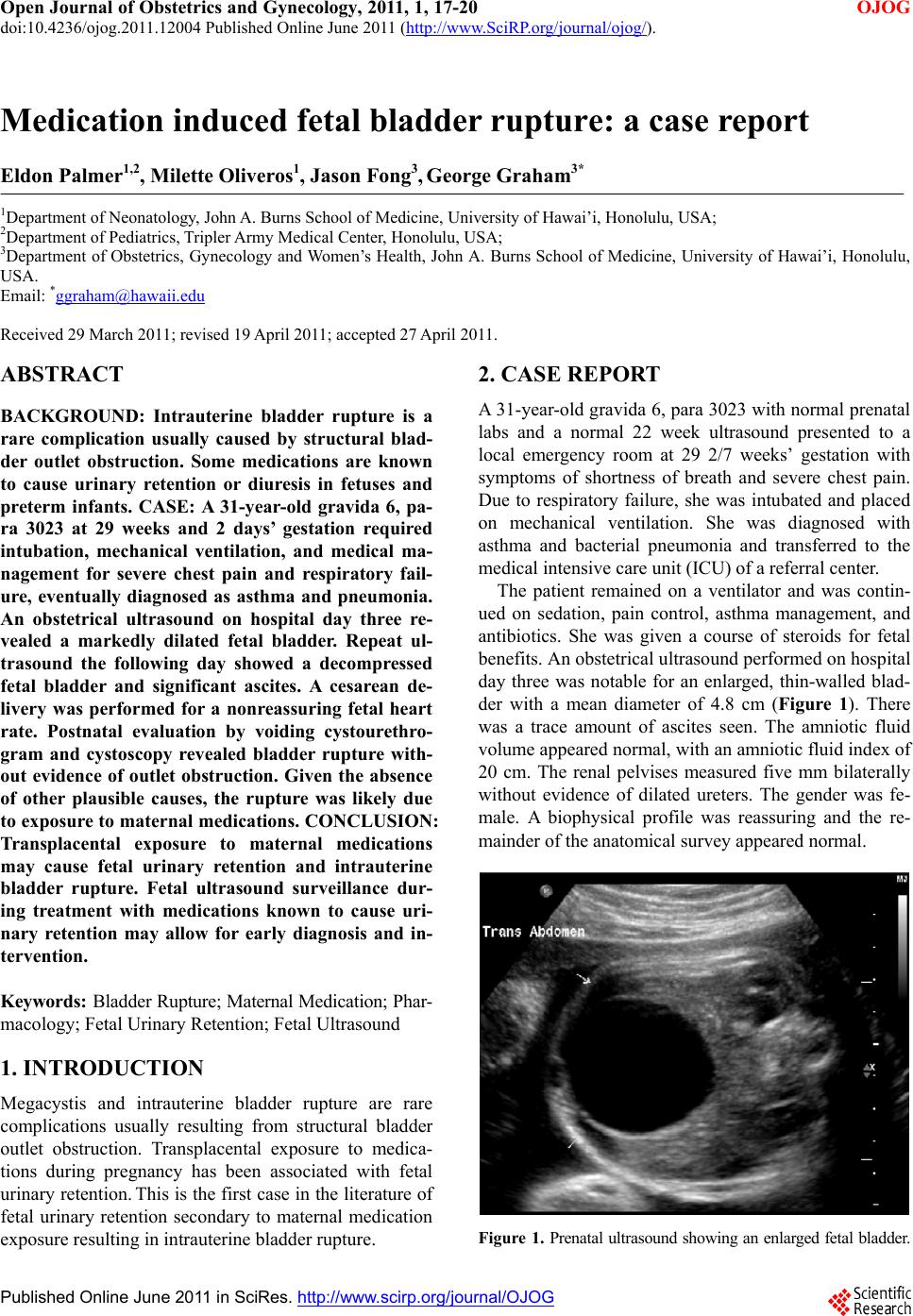
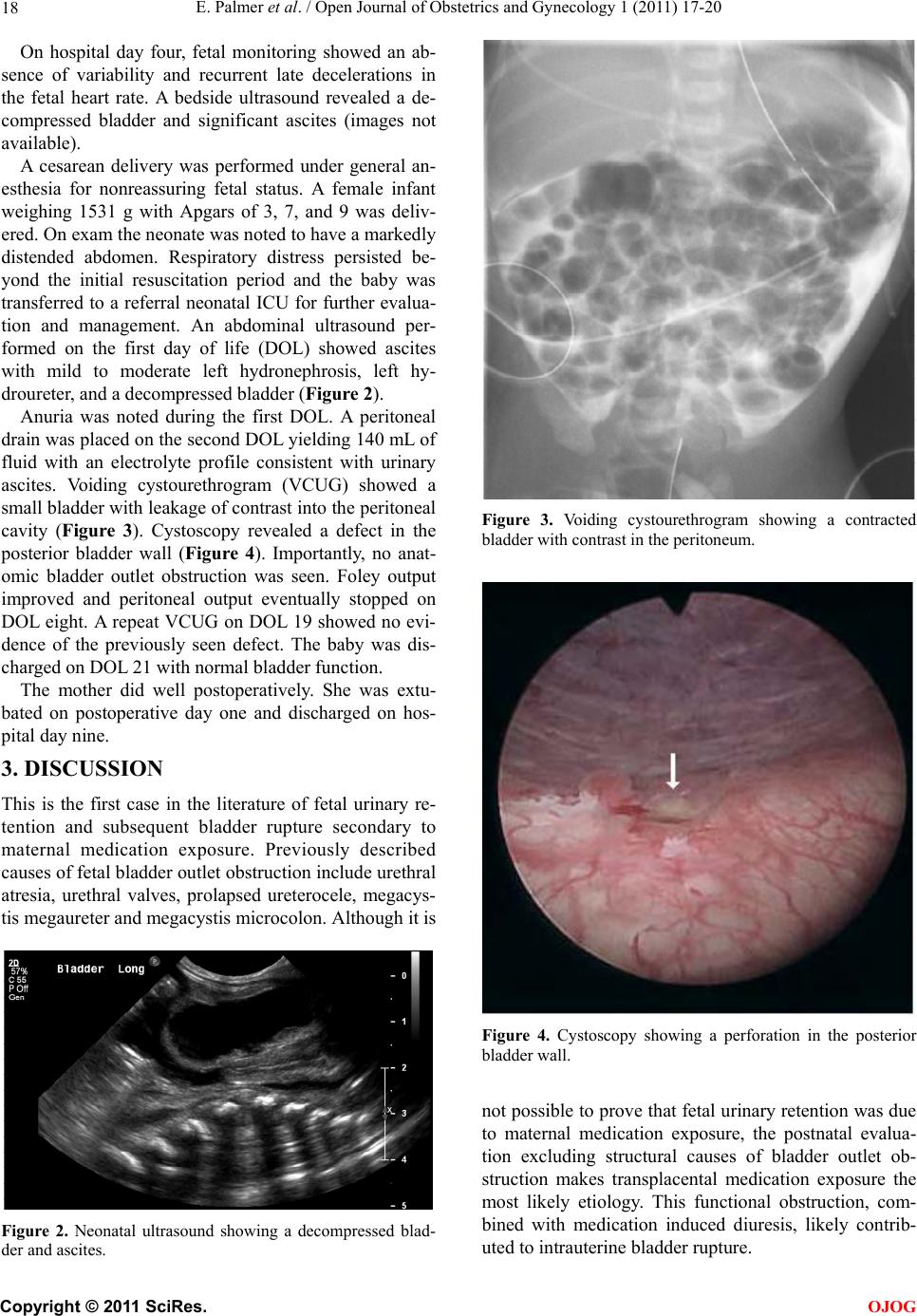
BACKGROUND: Intrauterine bladder rupture is a rare complication usually caused by structural bladder outlet obstruction. Some medications are known to cause urinary retention or diuresis in fetuses and preterm infants. CASE: A 31-year-old gravida 6, para 3023 at 29 weeks and 2 days’ gestation required intubation, mechanical ventilation, and medical management for severe chest pain and respiratory failure, eventually diagnosed as asthma and pneumonia. An obstetrical ultrasound on hospital day three revealed a markedly dilated fetal bladder. Repeat ultrasound the following day showed a decompressed fetal bladder and significant ascites. A cesarean delivery was performed for a nonreassuring fetal heart rate. Postnatal evaluation by voiding cystourethrogram and cystoscopy revealed bladder rupture without evidence of outlet obstruction. Given the absence of other plausible causes, the rupture was likely due to exposure to maternal medications. CONCLUSION: Transplacental exposure to maternal medications may cause fetal urinary retention and intrauterine bladder rupture. Fetal ultrasound surveillance during treatment with medications known to cause urinary retention may allow for early diagnosis and intervention.
Medication induced fetal bladder rupture: a case report

PDF) Bladder Exstrophy
Life, Free Full-Text

Uterine Rupture during Pregnancy: Can Laparoscopy be Performed Safely and Effectively?

Medication induced fetal bladder rupture: a case report
Paraplegia due to spinal meningioma during the third trimester of pregnancy: case report and literature review

Suzuka Okuno's research works University of Tsukuba, Tsukuba and

Urinary effects of morphine in preterm infants

PDF] Medication induced fetal bladder rupture: a case report

Medicina, Free Full-Text

Radiation and chemotherapy induced cystitis, Radiology Reference Article

PDF) Exposure to biological maternal sounds improves

Deepest vertical pocket method, Radiology Reference Article